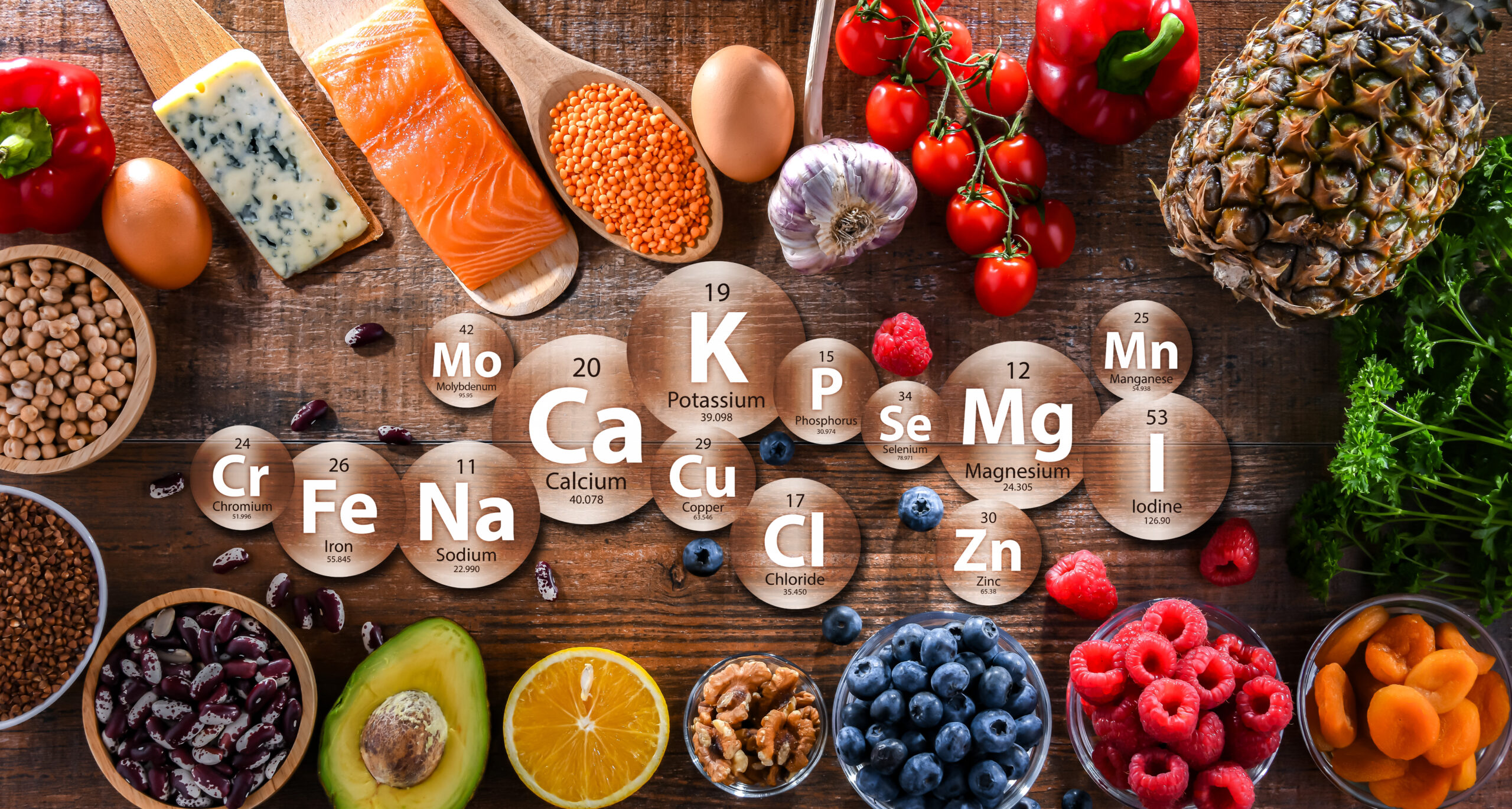//Blog
Macronutrients & Micronutrients
In our journey toward optimal health, understanding the basics of nutrition is key. Two categories play a central role in maintaining our health and well-being: macronutrients and micronutrients. Both are essential, yet each serves different functions within the body. In this blog, we’ll explore what they are, why they’re important, and how to ensure you’re getting the right balance of each.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients our bodies require in large amounts to provide us with energy and fuel for our daily activities. There are three primary types:
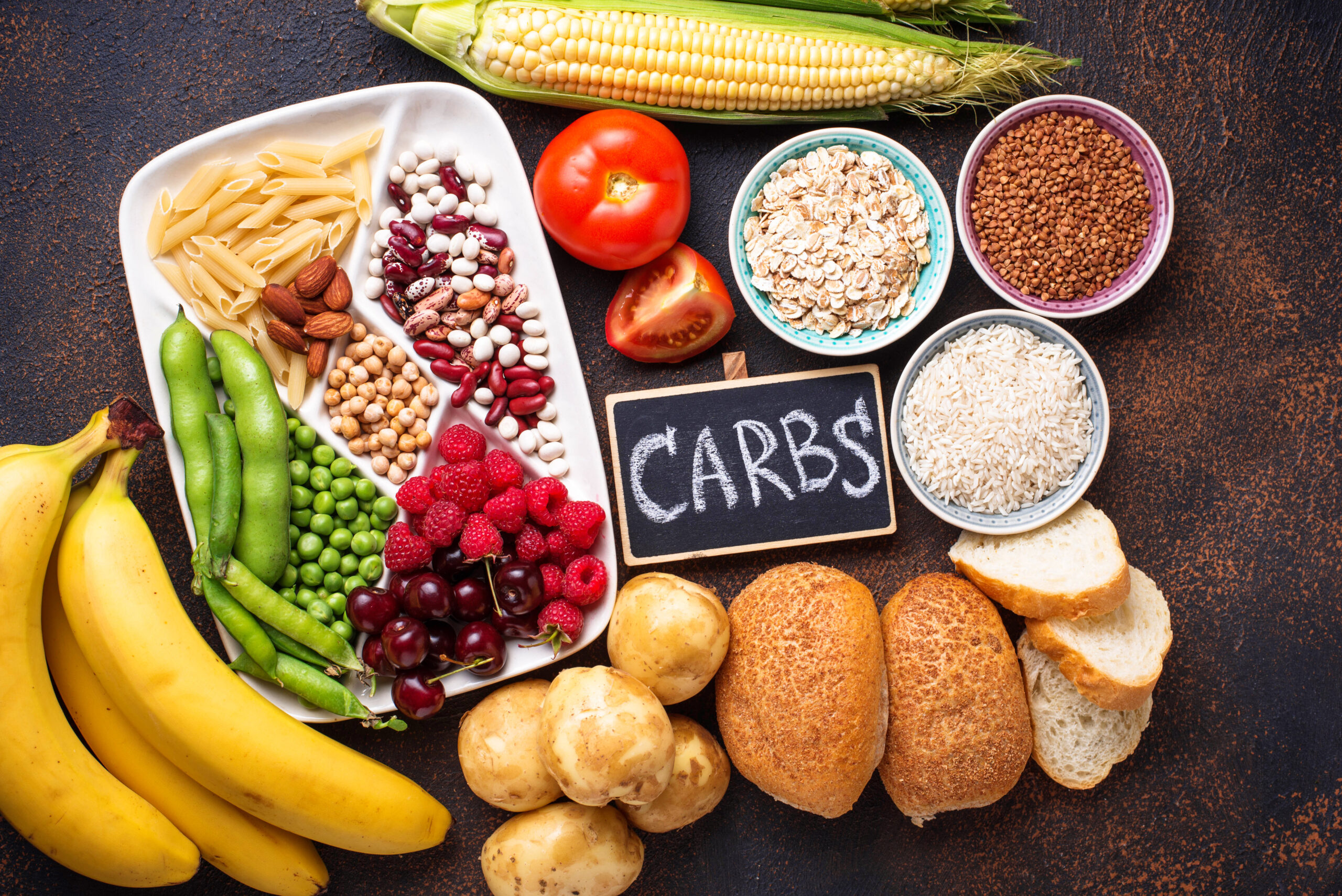
Carbohydrates
-
- Function: Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. They break down into glucose, which powers everything from brain function to physical activity.
- Sources: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products.
- Daily Intake: Carbs should make up about 45-65% of your daily calorie intake, although individual needs can vary based on activity level and dietary goals.
Proteins
-
- Function: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscles, skin, and organs. They also play a role in immune function and hormone production.
- Sources: Lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Daily Intake: Protein should constitute around 10-35% of your daily calories.

Fats
-
- Function: Fats support cell structure, protect organs, help with nutrient absorption, and serve as a reserve source of energy.
- Sources: Healthy fats can be found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
- Daily Intake: Fats should make up about 20-35% of your daily calorie intake, with an emphasis on unsaturated fats.
What Are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals that are needed in smaller amounts but are crucial for proper body function. They don’t provide energy directly but support critical bodily processes, such as metabolism, immunity, and bone health.
Vitamins
-
- Types: There are two types of vitamins: water-soluble (B-vitamins and Vitamin C) and fat-soluble (Vitamins A, D, E, and K).
- Functions: Vitamins help with immune function, energy production, blood clotting, and other physiological processes.
- Sources: Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fortified foods often contain a wide range of vitamins.
Minerals
-
- Types: Important minerals include calcium, magnesium, potassium, and trace minerals like iron, zinc, and selenium.
- Functions: Minerals help maintain electrolyte balance, build bone density, support heart health, and facilitate oxygen transport.
- Sources: Dairy, leafy greens, meat, fish, nuts, seeds, and grains.
The Importance of Balancing Macronutrients and Micronutrients
A healthy diet is all about balance. Each macronutrient has its own role, and a deficiency or excess in one can disrupt bodily functions. Similarly, micronutrient imbalances can lead to health issues such as weakened immunity, brittle bones, or anemia.
Some ways to achieve this balance include:
- Whole Foods Over Processed Foods: Whole foods, like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, are rich in both macro- and micronutrients.
- Variety is Key: Eating a variety of foods ensures a broader range of nutrients, reducing the risk of deficiencies.
- Supplements When Needed: If you’re unable to meet your nutritional needs through diet alone, supplements can be a helpful addition, especially for certain vitamins and minerals. Always consult a healthcare professional before adding any new supplement.
Why Do Macronutrient and Micronutrient Needs Vary?
Factors like age, lifestyle, health conditions, and physical activity levels influence individual needs. For example:
- Athletes may need higher protein and carbohydrate intakes to support energy and muscle repair.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women require additional iron, calcium, and folic acid for fetal development.
- Older adults may benefit from increased calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium to support bone health.
Finding the Right Balance for You
A balanced diet that incorporates all the essential macronutrients and micronutrients helps build a foundation for health, energy, and disease prevention. If you’re unsure about your nutritional needs, a healthcare professional or nutritionist can guide you in creating a personalized nutrition plan that suits your lifestyle and goals.
- Macronutrients (carbs, proteins, and fats) are needed in larger amounts and provide energy.
- Micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) are required in smaller amounts but are essential for bodily functions.
- Achieving a balance between macro- and micronutrients supports overall health and reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
For quality supplements, vitamins, and wellness products to support your dietary needs, explore our product offerings on The Health Pharmacy.